Climate Changes - Why Do We Care?
- mounting scientific evidence that temperature changes can happen fairly rapidly (e.g. warming by 10oC in Greenland in only few decades) (from oxygen isotope ratios in ice cores)
- mounting evidence that most recent change is caused by human impact
- current level of CO2 highest in last 800,000 years (evidence from ice cores)
- climate change may have negative impact on human life (financially and otherwise)
Examples for Possible Causes for Climate Change
- external: impacts, change in solar output, changes in Earth's position relative to Sun
- internal: changes in atmosphere and ocean chemistry, ocean circulation, volcanism, continental drift
The Atmosphere and Greenhouse Gases
- Review: Composition of Earth's Atmosphere (see Lecture 14)
- Nitrogen (N2): 78.08%
- Oxygen (O2): 20.95%
- Argon (Ar): 0.93%
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): 413ppm (2019)
(353 ppm in 1990; 380 ppm in 2005; 400 ppm in 2015) - Neon (Ne): 18ppm
- Helium (He): 5ppm
- Methane (CH4): 2ppm
- Krypton (Kr): 1ppm
- Water vapor (H2O): variable
- Review: Greenhouse Effect (see Lecture 14)
- Earth's equilibrium temperature is -18°C/0°F. The equilibrium T is the temperature the Earth has at the surface when insolation (received solar radiation) is in equilibrium with energy that is lost to space.
- Due to the presence of greenhouse gases (presently mainly CO2 and water vapor), the actual surface T is 33°C 59°F higher: 15°C/59°F.
Greenhouse Gases and Their Relevance
-
There is almost 200 times more CO2 in the atmosphere than CH4, yet the warming by CH4 is relatively important because its ability to trap heat is 20 times stronger. The contribution of each greenhouse gas to warming is2:
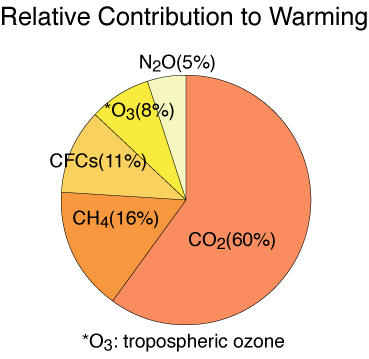 |
|
NB: The residence time of methane in the atmosphere is shorter (years-to-decades) than carbon dioxide (many decades to over a century). Reducing methane emission therefore will help limit global warming faster than reducing carbon dioxide emissions though their relative contribution has to be considered in discussions on emission reductions.
NB: CFCs are Chlorofluorocarbons. They are anthropogenic greenhouse gases, i.e. man-made, and do not occur naturally. CFCs were phased out by 1996 through the 1987 Montreal Protocol because they destroy the stratospheric ozone layer. However, the residence time of CFCs of several decades makes this a relevant greenhouse gas in the near future.
Radiative Forcing(1)
-
Technically, the radiative forcing is the difference of radiant energy received by Earth and energy radiated back to space. The radiative forcing is a measure over an area at the tropopause. A positive radiative forcing may induce surface warming, whereas
a negative radiative forcing may induce surface cooling.
- greenhouse gases have positive radiative forcing
- since the 1700s, changes in the sun's energy output may have produce a small positive forcing (~0.3 W/m2)
- ozone in the troposphere has positive radiative forcing (greenhouse gas)
- ozone in the stratosphere also has positive forcing (still a greenhouse gas); and it captures damaging UV radiation that would otherwise reach Earth's surface.
NB:The recent depletion of ozone in the stratosphere (ozone hole) leads to a net negative forcing at the top of the troposphere when compared to an intact atmosphere - water vapor is a greenhouse gas and has positive radiative forcing
- clouds (condensed water vapor) have negative radiative forcing because they reflect sunlight back to space that would otherwise reach Earth's surface
- aerosols in the lower atmosphere absorb heat, thus have positive radiative forcing
- aerosols in the upper atmosphere scatter and reflect sunlight, thus have negative radiative forcing
- large volcanic eruptions that inject sulfur-rich particles into the stratosphere that cause negative forcing for several years (estimates to more than offset the positive forcing by sun's increased output)
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) uses the term to weigh different contributing atmospheric factors (natural and anthropogenic) against each other to determine the net radiative forcing (see Lecture 22). Examples:
Feedback Mechanisms
- a secondary process that responds to and influences a change
- positive feedback mechanism: process that enhances change
- during global cooling, more snow and ice fall. This increases the albedo and enhances cooling.
- during global warming, snow and ice melt. This decreases the albedo and enhances warming.
- During warming, methane that resides below seafloor in ice lenses may melt. Methane gets released into the atmosphere and, being a potent greenhouse gas, accelerates warming.
- during global warming, warming air can hold more water vapor which is a greenhouse gas, enhancing warming
- negative feedback mechanism: process that counteracts and mutes change
- during warming, ice sheets melt. Cold fresh water floats on warmer ocean water. Warm ocean currents are diverted or slowed down which counteracts warming.
- during warming, climate gets wetter. More clouds form which increases albedo and counteracts warming.
- During cooling, climate gets drier. Less snow falls, albedo increases more slowly, counteracting the cooling.
Climate of the Early Earth
- Earth's early atmosphere is thought to have been similar to Venus' and Mars' current atmosphere that have changed very little over time; early CO2 content caused T to be an unpleasant 290°C, nearly half as hot as Venus is today
- Earth's atmosphere underwent dramatic change from CO2 rich to CO2 poor
- much is thought to have occurred through chemical weathering
- most CO2 is stored in limestones from chemical weathering, fossil shells, corals etc. as carbonate (e.g. Calcium Carbonate, CaCO3).
- much CO2 is now stored in the deep oceans (see Carbon Cycle; Box D)
- plants removed some CO2 and respired O2
Climate History of the Earth: Time Scale in Millions of Years
- rock profiles; e.g. different layers (strata) at one site inform us about local environmental fluctuations.
- local environmental change over time: can be result of climate fluctuation, continental drift, or tectonics; e.g. a place can be a marine environment at some point, a desert at another, and a glacial area at yet another point in time
- tell-tale indicators in sedimentary rocks to look for: fossilized bones; plant casts; corals; shells; coal; fossil dunes and soils
- Comparison of many profiles around the globe (corrected for continental drift!) give us an idea about the ancient global climate.
Possible Causes of Climate Change on this Time Scale
- changes in solar energy output on scales of millions to billions of years
- sun used to be fainter; its output increases 10% every 1 billion years
- predictions are that in 1 billion years Sun will be too hot for liquid water to exist on Earth Plate Tectonics
- position of land masses change over time so one spot can go through different climate stages
- extended rifting and volcanism influences regional to global climate
- variation in spreading rates influences global sea level
- large landmasses near pole leads to global cooling
- supercontinents covering large range of latitudes inhibit latitude-parallel
currents;
causes mixing of polar and tropical water -> more balanced climates Past Long-term Cold Periods
- pre-Cambrian (700-550 Mio yrs ago)
- late Carboniferous and early Permian (320-270Mio yrs ago)
this is the "late Paleozoic ice age" referred to in Box E. - Pleistocene (last 2.5 Mio yrs)
this is the "late Cenozoic ice age" referred to in Box E (cooling trend started 40 Mio yrs ago)
this period has been warmer than the other two cold periods - Possible Causes for Long-term Cold Climate:
- one or more large (super)continents near poles lead to higher albedo (positive feedback)
- few large continents do not disturb west-east ocean currents, so less exchange between latitudes
- disappearance of warm shallow seas during sea level drop
- less ocean evaporation leads to less water vapor (greenhouse gas!)
- less water vapor would also lead to less precipitation (dry!)
Past Long-term Warm Periods
- mid-Triassic (240-220 Mio yrs ago)
- late Jurassic through Cretaceous (170-65 Mio yrs ago)
- Eocene (50 - 40 Mio yrs ago); hottest climate in last 3 Ga
this is the "late Paleocene torrid age" referred to in Box E.
NB:Ga stands for billion years.
- Possible Causes for Long-term Warm Climate:
- smaller continents have less extreme climates
- smaller continents divert ocean currents north-south; drive global heat-conveyor
(though some closure of passages (e.g. Isthmus of Panama), blocking off warm currents, can have opposite effect) - melting ice sheets decrease albedo (positive feedback)
- extended large-scale volcanism injects greenhouse gases into atmosphere
-
Sun
Sea Level Changes
- on scales of millions to 100s of years
- sea level changes with global climate but also with plate tectonics
- Local sea level depends on:
- sediment input, compaction and subsidence (e.g. Mississippi Delta)
- isostatic load and rebound, e.g. Hudson Bay and coast along Canadian Shield have post-glacial rebound
- plate tectonics (e.g. fast spreading causes relatively shallow oceans, raising sea level)
- global climate (both warmer and colder)
- rises and falls with changes in ocean spreading rate
- falls during coastal tectonic uplift (e.g. in subduction zone)
- on scale of millions of years
- rises in warm climate as ice sheets melt
- falls in cold climates as water gets trapped in ice sheets
- falls in drier climates as less surface water runs off to feed streams, rivers
- on scale of 100s of years to 100s millions of years
- yearly: twice a year, spring tides are particularly strong (January, July) as Earth reaches perihelion and aphelion; though the change of the Moon-Earth distance also plays a role (perigee/apogee) and so affects the exact timing of the strongest spring tides; though not a scientific term, these King tides are significant in that they can cause significant coastal flooding even when no storm causes waves
- monthly: spring and neap tides as alignment of Sun, Earth, Moon changes
- daily: high and low tides caused by pull of Moon and Sun on Earth's surface
- on scales of hours to days: landfall of hurricanes and other big storms
- on scales of days: long-period swell from distant storms
Climate Variation in last 2 Million Years
-
The evidence for past climates on the scale of 10,000s of years comes from environmental climate indicators
- pollen composition
- tree rings (up to a few thousand years)
- sea and lake level changes
- ice cores; data for about last 800,000 years; air bubbles are trapped within ice as it forms; they contain the composition of the air (incl. CO2 at that moment; this effectively records climate (higher CO2 means warmer climate) as function of time, with oldest ice at the bottom and youngest ice at the top
- coral rings, oxygen isotopes in corals, marine sediments and ice sheets/glaciers (see Box C)
Ice Age Cycles
- climate has cooled in last 3 Mio yrs, compared to times before; at Vostok Station, Antarctica, average temperature may have declined by as much as 5°C (as evidenced from sediment cores)
- several ice ages and warm interglacial periods in Pleistocene epoch (last 2 Mio yrs)
- between 2.5 and 1 Mio yrs ago, ice age cycle was on order of 41,000 years; since then the ice age cycle occurred on a time scale of 100,000 years
- near the end of an ice age, extensive warming can occur over only few years!
- warming is accelerated through positive feedback mechanism of melting high-albedo snow and ice
- ice core data in particular provide a nearly continuous record of the coming and going of ice ages in the last 1 Mio years or so (some most recent cores reach ages up to 2 Mio years). These cores reveal rapid warming at the end of an ice age as compared to slow cooling into the next ice age (saw-tooth pattern)
The Last Major Ice Age
- 18,000-10,000 years ago
- includes several short warming and cooling periods (e.g. Younger Dryas, see above)
- ice sheet expanded over North America and Fennoscandia
- more mid-latitudinal rain
- sea level dropped considerably (130m/425ft)
- land bridge across Bering Strait facilitated migration from Eurasia into New World
- currently long-term cooling (tens of millions of years), but in an interglacial period with particularly severe short-term warming in last 100 years
- if current ice sheets were to melt, sea level would rise by 65m/210ft
- The Younger Dryas (12,900 - 11,700 years ago) briefly threw Earth back into an ice age after the last major ice age ended some 14,000 years ago. Rapid warming raised temperatures in Greenland by 15°C. Some cooling (account for about half of the drop in temperature) had already occurred in the previous 1500 years. But the drop in the Younger Dryas was rapid (within decades). The cause is thought to have come from a change in ocean circulation, more specifically a decline in the strength of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation which transports warm equatorial waters toward the North Pole. The 1500 years before the Younger Dryas had seen two major temperature swings (down and then back up) know as the Bølling (14,700-14,100 BP; cool) and the Allerød (13,900-12,900 BP; warm) events.
Possible Causes of Climate Change on this Time Scale
changes on time scales of less than a few Mio years cannot be caused by long-term plate tectonics!
- Milankovitch Cycles (changes in Earth's orbital parameters, see below) most important factor to explain last few ice ages; control amount of sunlight that Earth receives
- changes in solar energy output; on scales of years to 100,000s of years
- very extensive and/or long-lasting volcanism; on scales of years (SO2 output causing cooling) to possibly 1000s of years (CO2 output during very long-lasting, large-scale eruptions of flood basalts causing warming)
- changes in ocean circulation
The Milankovitch Cycles
- eccentricity of Earth's orbit around sun (100,000 years)
shape of Earth's orbit around the Sun changes between more or less elliptical - obliquity: tilt of Earth's spin axis (41,000 years) (21.5o to 24.5o; 23.5o at present)
tilt: axis of Earth's spin (or rotation axis) with respect to the normal (vector) of the ecliptic/Earth's orbital plane around the sun - precession of Earth's spin axis (25,000 years)
since Earth's spin axis is tilted, the gravitational force exerted by the Moon and the Sun on the spinning Earth causes the spin axis to rotate around the normal (vector) of Earth's ecliptic; NB: a more precise estimate of the precession period published by NASA would be 25,771.5 years.(4) - see NASA webpage on Milankovitch Cycles
- some scientific publications give a range between 19,000 and 23,000 years for a precession period of Earth's spin axis (5). But these are scientific details at a level not relevant to this class. It turns out the 'wobble' of Earth's spin axis is a combination of the axial precession (as mentioned above) plus the apsidal precession (periodicity of about 112,000 years), a wobble in Earth's orbit (due to Earth's interaction with Jupiter and Saturn). The combination of axial and apsidal precession make for an overall precession of about 23,000 years.
- the combined effect of all 3 Milankovitch cycles is a complicated function where not every decline in insolation triggers an ice age
- The Milankovitch cycles alone cannot account for the temperature variations associated with ice ages. The change in orbital parameters can cause temperature variations of up to 4 oC. However, observed changes are larger (5-7o C in coastal areas and 10-13o C inland). Therefore other mechanisms (e.g. including positive feedback) must be at work.
- Difference in season more important than total amount of insolation (need cool summers to avoid snow melt and mild winters that cause extensive snow fall)
Climate Variation on Scale of 10s - 100s of years
-
The evidence for past climates on the scale of 10s to 100s of years comes from historical (recorded) climate indicators
- tax records for crops
- paintings
- songs, epics and stories
- length of seasonal ice around Iceland
- names (e.g. Greenland due to warm period 800-1000)
- wine growth in England
- recorded advance and retreat of mountain glaciers
- modern measurements
Possible Causes of Climate Change on this Time Scale
- changes in ocean currents, decadal oscillations in Pacific and Atlantic (decades to hundreds of years?)
- interactions between oceans, atmosphere, ice sheets (years to decades?)
- volcanism; on scales of years (SO2 output causing cooling) to possibly 1000s of years (CO2 output during very long-lasting, large-scale eruptions of flood basalts)
- fertile crescent in Near East (5000-6000years ago) could be due to more solar activity
- variations in solar output (10s - 100s of years): some decades have less solar activity
- sun spot cycles on a scale of 11 years
- El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) and La Niña on a scale of few to 10 years
Short-term Cold Climates on 100-year Time Scale
- Maunder Minimum (~1700) during "Little Ice Age" (1400-1850); advance of glaciers; sea surrounding Iceland froze; rivers and canals in Europe froze; could have been caused by 0.25% less solar output/50-year absence of sunspot
- cooler first half of 20th century (prior to 1950s); correlates with less solar activity/sunspots
Short-term Warm Climates on 100 to 1000-year Time Scale
- for last 10,000 yrs, general interglacial period (warming) after last ice age
- 5000-6000 years ago (fertile crescent in Near East; global T was 2oC higher than today; possible cause: variation in solar output
- Greenland was green in AD 900, hence warmer than today!!
- current trend is warming on short scale (10s-100s of years) but cooling on long scale (millions of years)
- most recent trend: rapid warming at rate not seen in last 650,000 years
Sunspot Cycle: Climate change on the Scale of 10 years
- periodicity: about 11 years
- observed since 1749
- main source of periodic solar variation driving variations in space weather
- sunspots are darker but surrounding regions are hotter/brighter than average -> # of sunspots correlates with intensity of solar radiation
- variations are small (0.1%) compared to solar constant (solar output; 1366 W/m2)
- last maximum in 2000; last minimum in 2008 culminating with nearly no sunspot activity in August (see Earthwatch), nearly breaking a 100-year record
- overall, the sun is currently at a heightened level of sunspot activity and was last similarly active over 8000 years ago
El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) and La Niña: Climate change on the Scale of 10 years
(Spanish for "Christ Child") fishermen in Peru named the El Niño phenomenon after a time near Christmas when they sometimes (every few years) catch less fish than normal. During these years, this area also experiences droughts during the regular potato-growing season. Early farmers watched the Pleiades, a cluster of stars in the constellation of Taurus. If the stars were clearly visible, then there would be normal rain. If less stars were visible, the farmers knew a drought would be coming and delayed the sowing of potatoes.
- the main modern, satellite-based observation is that during an El Niño, equatorial waters in the East Pacific ocean are up to 5°C warmer than normal, whereas during a La Niña, surface waters are colder than normal
- The reason for the decrease in fish during an El Niño is the lack of nutrient-rich cold water that is usually upwelling from the deep East Pacific Ocean, but is cut off from reaching the surface by warm buoyant surface waters during an El Niño.
- During an El Niño condition warm water flows eastward from the central Pacific and cold nutrient-rich water remains at depth.
- El Niño also brings drought conditions to the Western Pacific (Indonesia, Papua New Guinea)
- El Niño causes rainfall in California but also droughts (e.g. rain in north and dry in south; rain in strong events but droughts in weak events).
- El Niño can change the global weather creating both more severe droughts and rainfall than normal (e.g. droughts in East Africa in the 1997 El Niño).
- for details in mechanisms, see lecture on air circulation (lecture 15)
- ENSO events have a periodicity of 4-7 years but the strength of events vary. A possible cause is the interaction with other oscillations (e.g. the Pacific Decadal Oscillation with a periodicity of 20-30 years.)
Observations:
Mechanisms:
BOX A: The Run-away Greenhouse
- warming atmosphere causes water to evaporate
- atmospheric water vapor increases greenhouse effect, accelerating evaporation
- without moderating negative feedback, Earth's temperature wound increase until all oceans are evaporated
- this chain-reaction is called the run-away greenhouse
- there is no evidence that Earth ever was a run-away greenhouse NB: Venus' dense CO2 atmosphere that keeps its surface at 480 deg C (900 deg F) is an example of a run-away greenhouse in which positive feedback mechanisms enhanced the warming.
Mars' atmosphere is too thin to produce a significant greenhouse.
BOX B: Glaciation
- Local past glaciation does not necessarily indicate that global climate has been colder: e.g. striation/glacial scratch marks on rocks found in Sahara desert can mean that either past climate was an ice house or that the Sahara was near the pole when the striations formed (the later was the case).
- Glaciation depends on:
- position of continent relative to pole
- precipitation
- global climate
- Glaciation has been relatively rare in Earth's history.
- More often than not, Earth has had ice free climates.
- The interplay of different factors into Earth's climate are non-linear and complicated. There is therefore currently no completely satisfactory theory that can account for Earth's past and present glaciation.
BOX C: Stratigraphic Indicators
- Stratigraphic Indicators for warm climate:
- tropical fossil reefs and micro-shells (most limestones)
- aluminum ore (bauxite) only found in tropical soil
- kaolinite (porcelain; a white clay that forms during weathering of feldspar - a mineral found in Granite - in a humid environment)
- evaporite minerals (halites and gypsum)
- Indicators for cold climate:
- erosion of glaciers sculpt tell-tale landscapes (U-shaped valleys)
- glaciers leave polished and grooved surfaces (striation)
- massive piles of debris (moraines)
- lack of fossils(?)
- Laws and Fossil Records
- uniformitarianism: processes that happen today are the same as those that happened in ancient times
- law of superposition: in an undisturbed stratigraphic sequence younger strata lie over older strata
- law of fauna assemblage: strata of like age can be recognized by the like assemblage of fossils they contain The validity of the last law was particularly important before physical dating methods (i.e. radiometric dating) was available.
Geologists use stratigraphic profiles, the layering of sediments and the fossils they find within the sediments, to estimate past climates and environments. This can only be done under certain circumstances that are formulated in laws. These include:
- Oxygen Isotope Ratios in Corals and Ice Cores:
- 16O/18O ratios; 18O has 2 neutrons more than 16O so is slightly heavier
- 18O evaporates more easily in warm water than in cold water
- cold water evaporating from oceans removes relatively more 16O, leaving behind 18O enriched water to include in corals and marine sediments; so 18O/16 ratio in corals is higher in cold climates
- glaciers trap more 16O so 18O/16 ratio in glaciers and ice sheets is lower in cold climates
- The situation is reversed in warm climate.
BOX D: The Carbon Cycle
- path of Carbon of special interest because CO2 is a greenhouse gas
- Carbon cycle describes the exchange of C between different reservoirs
- atmosphere: 720 Gt (gigatons)
- oceans: 38,400 Gt
- total inorganic: 37,400 (surface layer: 670; deep layer: 36,730)
- total organic: 1000
- terrestrial biosphere: 2000 Gt
- living biomass: 600-1000
- dead biomass: 1200
- sediments and rocks: 75,000,000 Gt
- sedimentary carbonates: > 60,000,000
- kerogens (geologically early stage of source rock for oil): 15,000,000
- aquatic biosphere: 1-2
- fossil fuels: 4130
- atmosphere-ocean exchange: 100-115 Gt
- decay of organic material: 50-60
- plant respiration: 40-60
- burning of fossil fuels: 6
- land clearing: 1-2.5
- volcanism: unknown
- photo synthesis: 100-120
- atmosphere-ocean exchange: 105-120
- weathering of rock: unknown, perhaps 0.6; most important in early Earth
- amount of CO2 in atmosphere is only 0.037%; but if CO2 and water vapor were absent in the atmosphere, Earth would be 33oC (59oF) colder; current average surface T is 15 oC/59oF.
- human activity, especially in the U.S. (25% of world's CO2 production!) is now increasing atmospheric CO2 at an alarming rate
- RESERVOIRS2:
- PATHWAYS INTO ATMOSPHERE3:
- PATHWAYS OUT OF ATMOSPHERE3:
BOX E: Outstanding Episodes2:
- Late Paleozoic Ice Age (360 - 260 Mio yrs ago): major ice age; one or more large supercontinent near poles lead to higher albedo, less water vapor, less precipitation, less greenhouse gases
- Late Paleocene Torrid Age (65-40 Mio yrs ago):equatorial zones slightly higher rainfalls than today but higher latitudes much warmer; southern oceans 10-15oC (18-27oF); less temperature difference in shallow and deep oceans and geographically led to less circulation; possibly catastrophic release of ice gas hydrates (methanes) from ocean floor
- Late Cenozoic Ice Age (last 40 Mio yrs): Earth undergoes long-term cooling trend; continental ice sheets 5-3 Mio yrs ago
References and Recommended Reading
- 1"Meteorology Today" by C. Donald Ahrens, Brooks/Cole Thomson Learning, 2003, ISBN: 0-534-39771-9
- 2 Patrick Abbott, 2005. "Natural Disasters". McGraw Hill
- 3 Falkowski et a., 2000. "The Global Carbon Cycle: A Test of Our Knowledge of Earth as a System". Science, vol 290 (13 October), 291-296
- 4 NASA webpage on Milankovitch Cycles
- (5)2013 publication in Nature on Milankovitch cycles
- "Earth's Climate, Past and Future" by William F. Ruddiman, 2000. W.H. Freeman and Company, ISBN: 0-7167-3741-8
Not required to pass the tests, but for the interested souls:
Also, food for thought to discuss climate change and human impact in this and future classes
"State of the World" by The Worldwatch Institute, W.W. Norton and Company.
Topics change from year to year but the 2004 book (ISBN: 0-393-32539-3) was on consumerism and globalization, waste/recycling of resources, catch-up of developing countries, water productivity and increasing shortage. Earlier books were on energy resources, greenhouse effect, Kyoto Protocol and the spread of and fight against diseases.
